A newly discovered cyber-espionage framework, dubbed EggStreme, has been deployed against a Philippine military contractor in a sophisticated intrusion attributed to a Chinese APT group.
Unlike conventional malware, EggStreme employs a multi-stage, fileless architecture that injects malicious components directly into memory and exploits DLL sideloading to execute payloads under the guise of trusted Windows binaries, thereby operating quietly.
The intrusion begins when a compromised SMB share delivers a logon script that drops a legitimate WinMail.exe and a malicious mscorsvc.dll into the user’s Windows Mail directory.
When WinMail.exe runs, it loads the attacker’s mscorsvc.dll instead of the genuine .NET service library, triggering the first stage loader—EggStremeFuel.
This component fingerprints the host, establishes a reverse shell via cmd.exe, and manages an encrypted configuration file in %APPDATA%MicrosoftWindowsCookiesCookies.dat, enabling C2 updates through RC4 encryption.
To maintain persistence, the adversary hijacks disabled or manual-start Windows services—MSiSCSI, AppMgmt, and SWPRV either by replacing the service binary or altering its ServiceDLL registry value.
Each service is configured with SeDebugPrivilege and launched to run EggStremeLoader, which decrypts two RC4-encrypted segments, EggStremeReflectiveLoader and EggStremeAgent from C:Windowsen-USielowutil.exe.mui.
These segments are decrypted in memory and injected into trusted processes (winlogon.exe, MsMpEng.exe, or explorer.exe), ensuring that no decrypted payload touches disk.
EggStremeAgent, the framework’s core implant, establishes mutual TLS gRPC communication with C2 and exposes a 58-command interface. Capabilities include system fingerprinting, file and directory operations, network enumeration, privilege escalation, shellcode execution, LSASS process injection, and GZIP-based exfiltration.
The agent monitors for WTS_EVENT_LOGON, decrypts the EggStremeKeylogger, and injects it into each new explorer.exe session to capture keystrokes, clipboard data, and network adapter changes, logging the results in an encrypted thumb drive cache file.
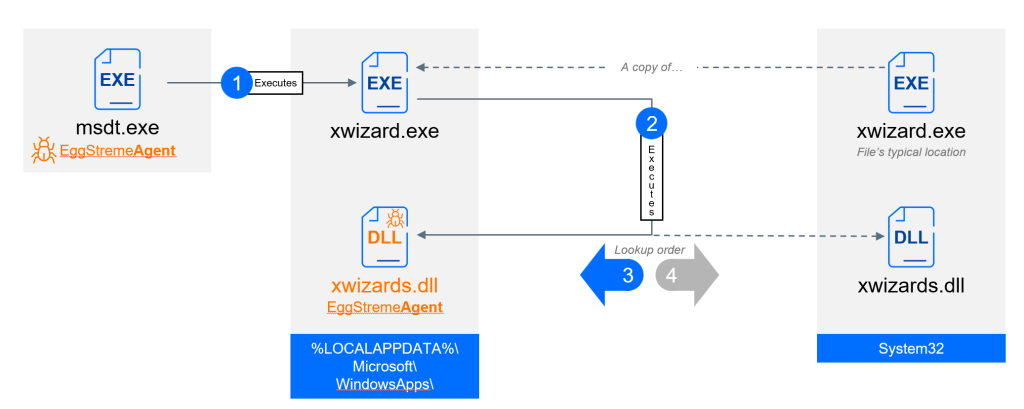
A secondary backdoor, EggStremeWizard, uses a relocated xwizard.exe and malicious xwizards.dll to sideload a lightweight reverse-shell implant. This ensures redundancy by maintaining file transfer and remote command capabilities via multiple C2 servers.
Additionally, the Go-based Stowaway proxy tool was deployed to pivot within the network, bypassing segmentation by exposing an internal proxy on port 8531, authenticated with a hardcoded secret.
Public IOCs—including domains whosecity[.]org and webpirat[.]net, and IPs 154.90.35.190 and 45.115.224.163—are available in the EggStreme IOC GitHub repository.
Defenders should monitor for unusual service binaries, DLL sideloading events, fileless reflective injection patterns, and outbound gRPC connections.
Implementing application whitelisting, restricting legitimate LOLBin usage, and enabling EDR/XDR telemetry on gRPC and reflective injection activity can help detect and disrupt this stealthy fileless threat.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates
