PromptLock, the AI-powered proof-of-concept ransomware developed by researchers at NYU Tandon and initially mistaken for an active threat by ESET, is no longer an isolated example: Google’s latest report shows attackers are now creating and deploying other malware that leverages LLMs to operate and evade security systems.
A step toward more autonomous and adaptive malware
Google’s threat intelligence analysts have observed several instances of AI-powered malware being used in the wild:
- QuietVault is a credential stealer that targets GitHub and NPM tokens, but also leverages an AI prompt and on-host installed AI CLI tools to search for other potential secrets on the infected system to exfiltrate.
- PromptSteal (used by Russian APT28, aka Fancy Bear) is a data miner that uses the Hugging Face API to query Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct to generate one-line Windows commands, which it then executes to collect and exfiltrate data.
- FruitShell is a reverse shell that contains hard-coded prompts aimed at bypassing detection/analysis by LLM-powered security systems.
The above-mentioned PromptLock and PromptFlux (a dropper) are both considered experimental. The former uses an LLM to dynamically generate and execute malicious Lua scripts at runtime, and the latter uses the Google Gemini API to rewrite its own source code on an hourly basis to evade detection.
“Adversaries are no longer leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) just for productivity gains, they are deploying novel AI-enabled malware in active operations. This marks a new operational phase of AI abuse, involving tools that dynamically alter behavior mid-execution,” Google’s analysts pointed out.
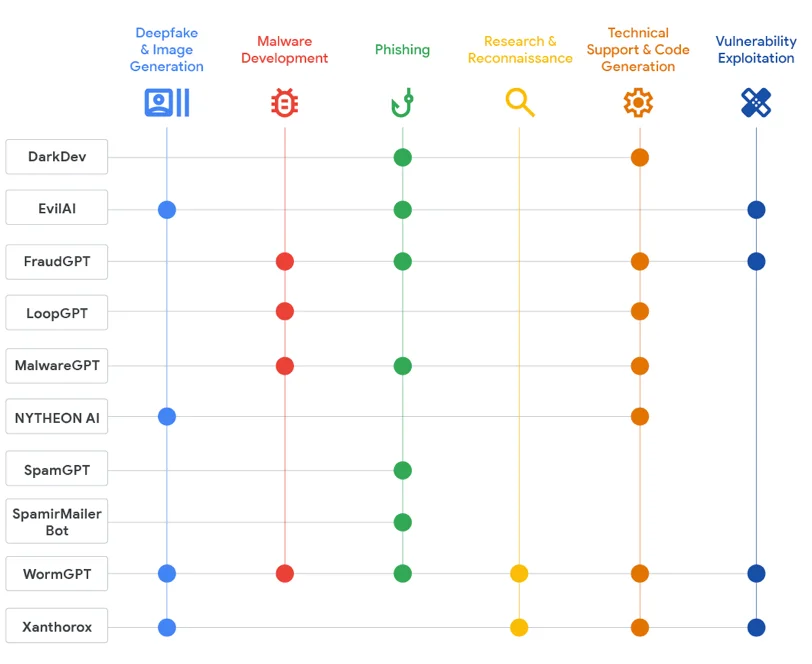
They also found that underground marketplaces catering to cybercriminals have a healthy selection of illicit AI offerings, with various alleged capabilities:
AI offerings advertised in underground forums and their capabilities (Source: Google Threat Intelligence Group)
AI as a skills enhancer
Like Anthropic before it, Google has outlined how various threat actors misused its LLM to increase productivity during all attack stages.
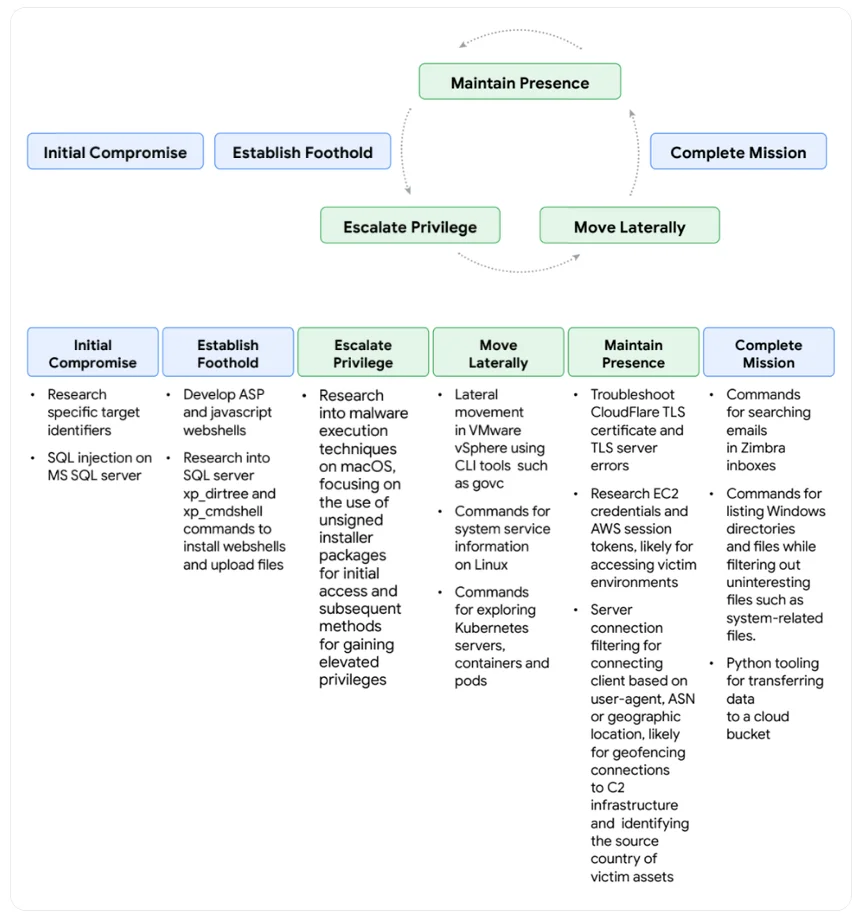
A China-nexus threat actor misused Gemini for crafting lure content, building technical infrastructure, and developing tooling for data exfiltration. An Iranian state-sponsored threat actor used it to research how to develop custom malware.
Google admitted that both managed to bypass Gemini’s reluctance to provide responses – the China-nexus actor by claiming to be a participant in a capture-the-flag (CTF) exercise, and the Iranian threat actor by posing as a student working on a university project, paper or article. (Google says it has since strengthened protections against these techniques.)
How a China-nexus threat actor misused Gemini across the attack lifecycle (Source: Google Threat Intelligence Group)
“Threat actors continue to adapt generative AI tools to augment their ongoing activities, attempting to enhance their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to move faster and at higher volume,” the analysts noted.
“For skilled actors, generative AI tools provide a helpful framework, similar to the use of Metasploit or Cobalt Strike in cyber threat activity. These tools also afford lower-level threat actors the opportunity to develop sophisticated tooling, quickly integrate existing techniques, and improve the efficacy of their campaigns regardless of technical acumen or language proficiency.”

Subscribe to our breaking news e-mail alert to never miss out on the latest breaches, vulnerabilities and cybersecurity threats. Subscribe here!