A newly identified information-stealing malware dubbed Shuyal Stealer has emerged as one of the most versatile and invasive threats currently circulating in the cybercriminal ecosystem.
Unlike typical stealers that target a few mainstream browsers, Shuyal is engineered to harvest data from 19 different browser platforms, including Chrome, Edge, Brave, Opera, Vivaldi, Yandex, Waterfox, and even privacy-focused options like Tor.
This broad targeting exponentially increases its potential attack surface and effectiveness in stealing credentials from users across different environments.
Shuyal Stealer’s data theft mechanism extends far beyond harvesting browser-stored credentials. Upon execution, the malware performs deep system reconnaissance through Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) commands to collect granular details such as disk drive models, input peripherals, and display configurations.
This detailed fingerprinting enables attackers to tailor follow-on attacks or perform identity correlation based on system metadata.
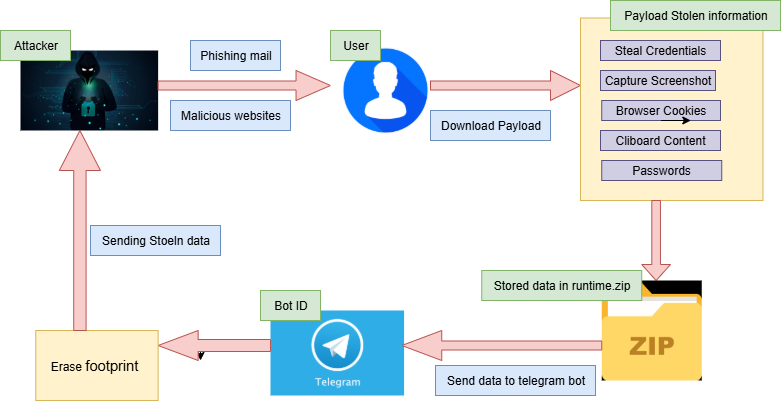
In its credential theft routine, Shuyal executes an SQL query SELECT origin_url, username_value, password_value FROM logins across browser SQLite databases to extract usernames, URLs, and encrypted passwords.
It also captures screenshots using. GdiplusStartup, BitBlt, and GdipSaveImageToFile APIs, while the clipboard contents are extracted via OpenClipboard and GetClipboardData.
The stolen data, including Discord tokens, is stored within directories such as runtimebrowsertokens.txt and runtimeclipboardclipboard.txt for staged exfiltration.
To compress and exfiltrate the stolen information, Shuyal employs a PowerShell script that archives the collected files runtime.zip before transmitting them to the attacker via a Telegram bot API.
The malware’s command sequence leverages a hardcoded bot token and chat ID, pointing to the endpoint api.telegram[.]org/[bot]7522684505.../sendDocument?chat_id=-1002503889864, effectively transforming Telegram into a covert command-and-control channel.
Once data transfer completes, it self-deletes files and traces through a batch script named util.bat to evade analysis.
Shuyal Stealer showcases advanced evasion and persistence features designed to keep it hidden from users and security tools.
It disables Windows Task Manager by setting the registry value DisableTaskMgr to 1 and forcibly terminates active taskmgr.exe instances using TerminateProcess.
To persist after reboot, it quietly replicates itself to the Windows Startup folder via the CopyFileA API, ensuring consistent execution on startup.
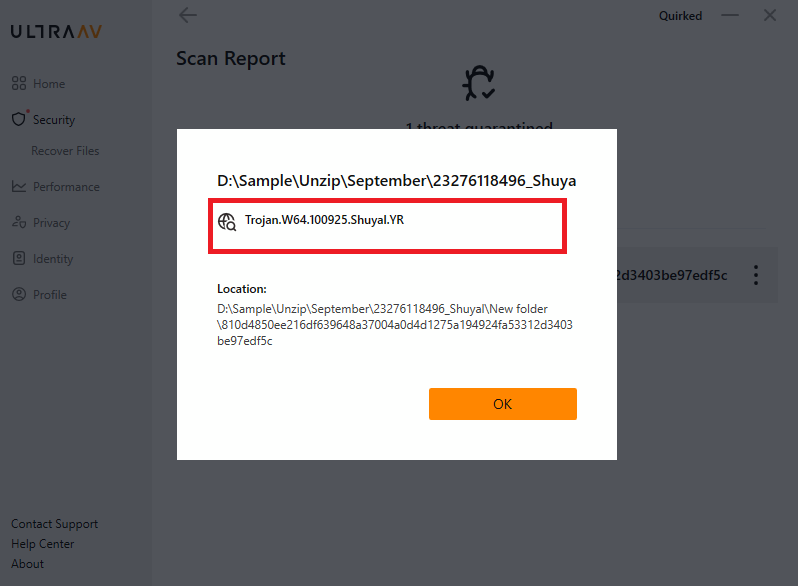
The malware sample analyzed, compiled as a 64-bit C++ executable (SHA-256: 8bbeafcc91a43936ae8a91de31795842cd93d2d8be3f72ce5c6ed27a08cdc092), has been detected under the name Trojan.W64.100925.Shuyal.YR by UltraAV antivirus.
Key artifacts include files such as runtime.zip, saved_passwords.txt, and screenshot output ss.png.
Security researchers warn that Shuyal’s combination of broad browser coverage, deep system profiling, and Telegram-based exfiltration makes it a formidable threat capable of large-scale credential compromise and sustained stealth operations.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates
